|
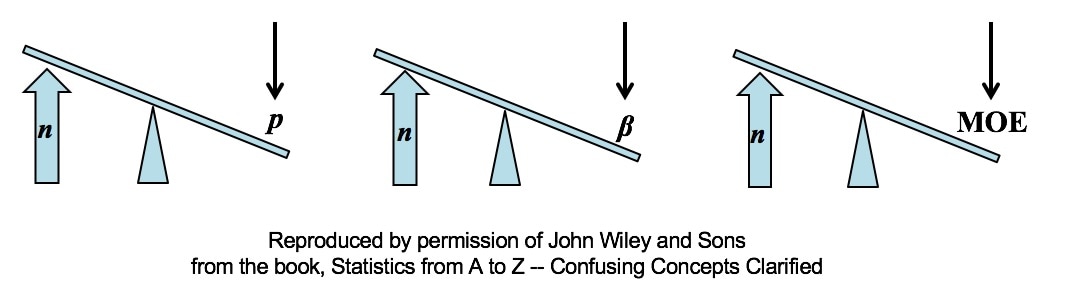
All other things being equal, an increase in Sample Size (n) reduces all types of Sampling Errors, including Alpha and Beta Errors and the Margin of Error.
A Sampling "Error" is not a mistake. It is simply the reduction in accuracy to be expected when one makes an estimate based on a portion – a Sample – of the data in Population or Process. There are several types of Sampling Error. Two types of Sampling Errors are described in terms of their Probabilities:
All three types of Sampling Error are reduced when the Sample Size is increased. This makes intuitive sense, because a very small Sample is more likely to not be a good representative of the properties of the larger Population or Process. But, the values of Statistics calculated from a much larger Sample are likely to be much closer to the values of the corresponding Population or Process Parameters. For more on p, see my video P, the p-value. In the future, there will also be videos on Alpha and Beta Error, the Margin of Error, and Confidence Intervals. You can subscribe to the channel to be notified.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorAndrew A. (Andy) Jawlik is the author of the book, Statistics from A to Z -- Confusing Concepts Clarified, published by Wiley. Archives
March 2021
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed