|
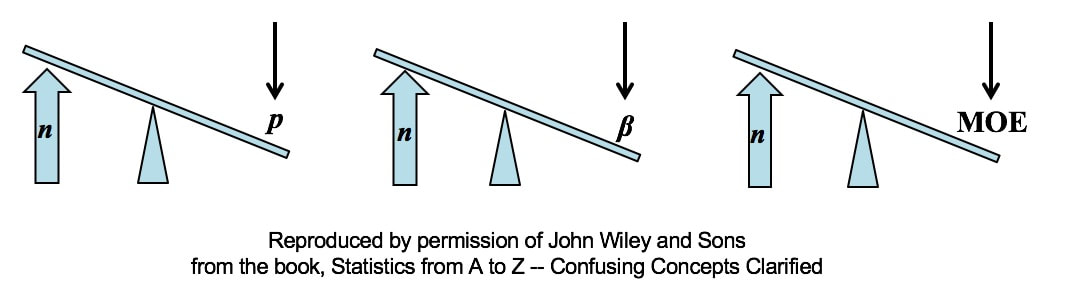
All other things being equal, an increase in Sample Size (n) reduces all types of Sampling Errors, including Alpha and Beta Errors and the Margin of Error. A Sampling "Error" is not a mistake. It is simply the reduction in accuracy to be expected when one makes an estimate based on a portion – a Sample – of the data in Population or Process. There are several types of Sampling Error.
Two types of Sampling Errors are described in terms of their Probabilities:
All three types of Sampling Error are reduced when the Sample Size is increased. This makes intuitive sense, because a very small Sample is more likely to not be a good representative of the properties of the larger Population or Process. But, the values of Statistics calculated from a much larger Sample are likely to be much closer to the values of the corresponding Population or Process Parameters For more on the statistical concepts mentioned here (p, β, MOE, Confidence Intervals, Statistical Errors, Samples and Sampling), please see my book or my YouTube channel -- both are titled Statistics from A to Z -- Confusing Concepts Clarified.
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorAndrew A. (Andy) Jawlik is the author of the book, Statistics from A to Z -- Confusing Concepts Clarified, published by Wiley. Archives
March 2021
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed