|
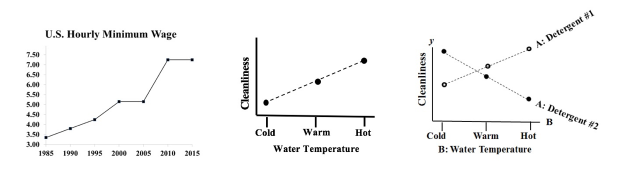
A Line Chart uses lines to connect points that have adjacent values on the horizontal axis. It is often used to illustrate trends, with the horizontal axis representing time.
It is also used to graph cause-and-effect, in which the x Variable (horizontal axis) is the Factor which causes the effect in the y Variable (vertical axis). In the center chart above, an increase in the Factor Variable, water temperature, causes an increase in the Effect Variable, cleanliness. This is used in Regression analysis and in the Designed Experiments which are conducted to test a Regression Model. The rightmost chart combines two line charts into one. It has the same x and y Variables as the center chart, but it adds a second Factor (x) Variable, Detergent type. So, there are two lines, connecting two sets of data points. In 2-Way ANOVA, crossing lines indicate that there is an Interaction between the two Factors. In this case, an increase in temperature has the opposite effect for the two detergent types – it makes Detergent #1 do better, and it makes Detergent #2 do worse. If the lines were parallel or did not cross, then there would be no Interaction. In a similar fashion, a Line Chart can help differentiate between Observed and Expected Frequencies in a Chi-Square test for Goodness of Fit. Reproduced by permission of John Wiley and Sons, Inc. from the book, Statistics from A to z -- Confusing Concepts Clarified
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorAndrew A. (Andy) Jawlik is the author of the book, Statistics from A to Z -- Confusing Concepts Clarified, published by Wiley. Archives
March 2021
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed